- _nosay
ServletConfig对象
2017-11-19 12:14:13
ServletConfig对象到底是什么?
servletConfig对象是它所对应的Servlet对象的相关配置信息
特点:
1.每一个servlet对象都有一个ServletConfig对象和它相对应。
2.ServletConfig对象在多个Servlet对象之间是不能共享的。
常见的ServletConfig对象的方法
1.getInitParameter(String name):返回一个初始化变量的值。
2.getInitParameterNames():返回Servlet初始化参数的所有名称。
3.getServletContext():获取ServletContext对象。
4.getServletName():获取Servlet的name配置值。
测试代码
web.xml内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> <servlet> <servlet-name>helloServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>net.zixue.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>utf-8</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>helloServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/test</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
HelloServlet文件内容:
package net.zixue.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
super.init();
ServletConfig servletConfig = this.getServletConfig();
String encoding = servletConfig.getInitParameter("encoding");
System.out.println("encoding:" + encoding);
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.printf("接收到get请求!");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.printf("接收到post请求!");
}
} 执行结果
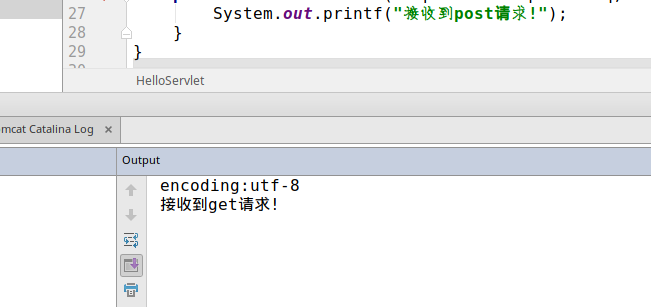
ServletContext定义:ServletContext即Servlet上下文对象,该对象表示当前的web应用环境信息.
获取ServletContext对象:
1.通过ServletConfig的getServletContext()方法可以得到ServletContext对象
2.HttpServlet中直接通过this.getServletContext()获取
域对象(域对象就是在不同资源之前来共享数据,保存数据,获取数据),ServletContext对象通常称为Context域对象.ServletContext是我们学习的第一个域对象
ServletContext对象的应用:
1.使用ServletContext获取整个web项目初始化参数
在web.xml中配置初始化参数
<context-param> <param-name>参数名</param-name> <param-value>参数值</param-value> </context-param>
String getInitParameter(String name):根据名称获取初始化参数
Enumeration getInitParameterNames();获取所有初始化的参数名称.
2.使用ServletContext在多个Servlet中共享数据
void setAttribute(String name, Object object):存放数据
Object getAttribute(String name);获取数据
void removeAttribute(String name);删除数据
3.使用ServletContext读取web项目中的资源文件
实际操作使用,首先在web.xml中定义一个全局context-param,具体代码如图
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> <context-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>utf-8</param-value> </context-param> </web-app>
创建一个Servlet,具体代码如下:
package com.nosay.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "Test1Servlet",urlPatterns = "/test1")
public class Test1Servlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("你执行了test1中的doGet方法");
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
String encoding = servletContext.getInitParameter("encoding");
System.out.println(encoding);
}
}运行如图:
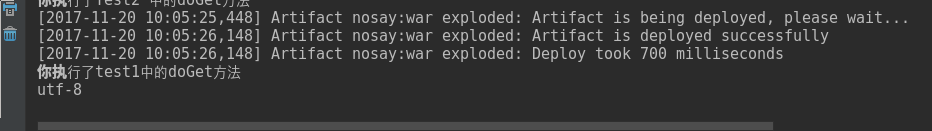
这样就成功取得了全局的context-param的值
在多个Servlet之间共享参数
Test2Servlet代码如下:
package com.nosay.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "Test2Servlet",urlPatterns = "/test2")
public class Test2Servlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String data = "share value";
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("name",data);
System.out.println("已经生成了共享name值");
}
}Test3Servlet代码如下
package com.nosay.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "Test3Servlet",urlPatterns = "/test3")
public class Test3Servlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String name = (String)this.getServletContext().getAttribute("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
}这样,先访问test2然后再访问test3,如图所示
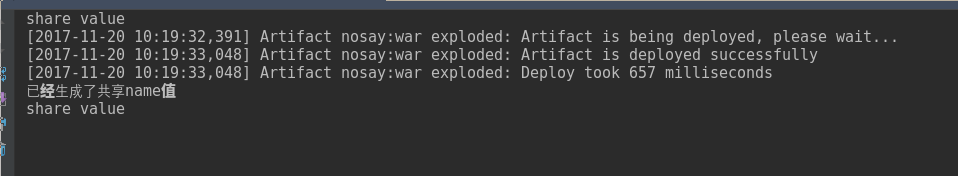
ServletContext-读取项目的资源文件:
在web项目的实际开发中,我们经常会用到数据库之类的,那么数据库有很多连接信息,这些连接信息我们需要配置到一个配置文件中,然后在调用的时候,可以通过ServletContext对象去读取配置信息,那现在我们去创建一个数据库的配置文件:db.properties,具体内容如下:
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306 name=name password=password
创建Test4Servlet文件,相关代码如下
package com.nosay.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
@WebServlet(name = "Test4Servlet",urlPatterns = "/test4")
public class Test4Servlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(url);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(password);
}
}执行结果如图:
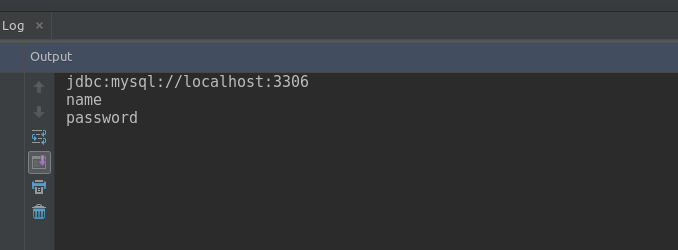
这样就成功拿到了相关文件的配置信息